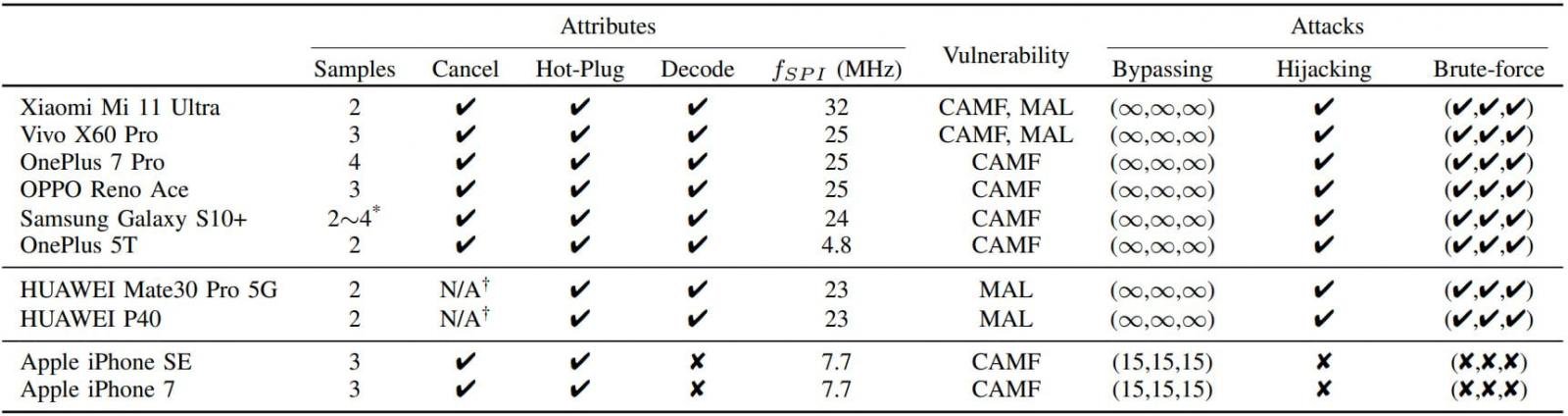
Chinese researchers have found that many Android smartphones are vulnerable to fingerprint protection hacking. A new method of brute force attacks Bruteforce is a method of hacking by sequentially iterating through all possible options. named BrutePrint.
BrutePrint uses two zero-day vulnerabilities to increase the number of fingerprint login attempts indefinitely, whereas usually a smartphone asks you to enter a password code after several unsuccessful attempts.The exploit was confirmed on six popular Android smartphones, including Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra and OnePlus 7 Pro, as well as Huawei P40 on HarmonyOS and iPhone with a fingerprint scanner. If in the case of Android and HarmonyOS it was possible to get an infinite number of login attempts by the scanner, then on the iPhone this method can increase the number of attempts to only 15 instead of the usual 5. This is not enough for hacking.
After receiving endless attempts, a simple device consisting of two boards and a manipulator feeds the smartphone fingerprint images from the databases. They are processed so that the smartphone system considers them images from the scanner and compares them with its database. In some cases, researchers even managed to manipulate the cutoff value of false positive results to speed up the selection.
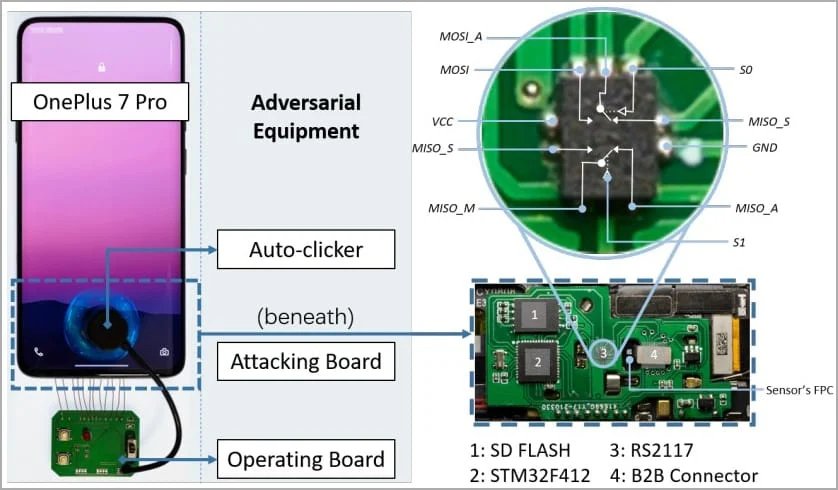
It is noted that for hacking, an attacker requires physical access to the device, as well as fingerprint databases (from open academic sources or biometric data leaks). The equipment needed for the exploit is inexpensive: it can be assembled for about $ 15.
However, hacking also takes a lot of time: from 2.9 to 13.9 hours if the user has registered only one finger for scanning. The more fingerprints there are in the smartphone's memory, the faster BrutePrint is executed: it can take less than an hour to hack.
The use of such hacking systems has not yet been reported. Although most users are unlikely to be the target of such attacks, this technology can be dangerous for stolen devices that have not turned on the missing mode.